- 9975035364
- [email protected]
ECG /2D ECO/ STRESS TEST
What is ECG?
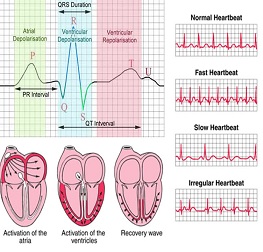
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that checks for problems with the electrical activity of your heart. An EKG translates the heart's electrical activity into line tracings on paper. The spikes and dips in the line tracings are called waves. The heart is a muscular pump made up of four chambers. The two upper chambers are called atrium, and the two lower chambers are called ventricles. A natural electrical system causes the heart muscle to contract and pump blood through the heart to the lungs and the rest of the body. An electrocardiogram(ECG) is a test that measures the electrical signals that control heart rhythm. It is called a 12-lead ECG because it examines the electrical activity of the heart from 12 points of view. This is necessary because no single point (or even 2 or 3 points of view) provides a complete picture of what is going on. The test measures how electrical impulses move through the heart muscle as it contracts and relaxes.
Why It Is Done?
- An electrocardiogram (ECG)is done to.
- Check the heart's electrical activity.
- Find the cause of unexplained chest pain, which could be caused by a heart attack, inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart (pericarditis), or angina.
- Find the cause of symptoms of heart disease, such as shortness of breath, dizziness, fainting, or rapid, irregular heartbeats (palpitations).
- Find out if the walls of the heart chambers are too thick (hypertrophied
- Check how well medicines are working and whether they are causing side effects that affect the heart.
- Check how well mechanical devices that are implanted in the heart, such as pacemakers, are working to control a normal heartbeat.
- Check the health of the heart when other diseases or conditions are present, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, cigarette smoking, diabetes, or a family history of early heart disease.
How is the ECG performed?
A patient generally lies on an examination table, and 10 electrodes (or leads) are attached to the arms, legs, and chest of the patient. The electrodes detect the electrical impulses generated by the heart, and transmit them to the ECG machine. The ECG machine produces a graph (the ECG tracing) of those cardiac electrical impulses. The electrodes are then removed. The test takes less than 5 minutes to perform.
What information can be gained from the ECG?
- From the ECG tracing, the following information can be obtained
- The heart rate.
- The heart rhythm
- Whether there are conduction abnormalities (abnormalities in how the electrical impulse spreads across the heart).(abnormalities in how the electrical impulse spreads across the heart).
- Whether there has been a prior heart attack.
- Whether there may be coronary artery disease
- Whether the heart muscle has become abnormally thickened.

STRESS TEST :
This test is used to determine if blood reaches the heart muscle from coronary arteries. Radioisotopes are radioactive elements like Cardiolite or Thallium. This test is combined with exercise stress test on the treadmill or a bicycle. This is to gently tire the heart and detect disease, which cannot be detected without exercise. In case the patient cannot walk, medicines are used to make the heart beat faster and put it under stress. When the patient is near the highest target exercise, a very small amount of radioisotope is injected into the blood stream. The patient lies on scanning table which has a special camera on top. The camera detects whether radioisotope passes from the blood vessels to the heart muscle. This information is converted into images. If after exercise, the heart muscle tissue does not receive enough radioisotopes, it means that part of the heart has less than adequate blood supply. This result is recorded as images. This is then compared to the images of the heart at rest (without exercise). The two series of images are compared by the cardiologist to determine if the heart muscle has deficient blood supply.
2D ECHO :
2D Echocardiography or 2D Echo of heart is a test in which ultrasound technique is used to take pictures of heart. It displays a cross sectional ‘slice’ of the beating heart, showing chambers, valves and the major blood vessels of heart. ‘Doppler’ is a special element of this ultrasound exam that assesses flow of blood in the heart.
How is 2D Echo done?
Patient is made to change in a front open robe and a colourless gel is applied to the chest area. Then he is asked to lay on his left side as the technician moves the transducer across the various parts of his chest to get specific/desired views of the heart. Instructions may also be given to the patient to breathe slowly or to hold it. This helps in getting superior quality pictures. The images are viewed on the monitor and recorded on paper, video or DVD. The cardiologist later reviews and interprets the recordings.
What it detects?
Echocardiography is a significant tool in providing the physician important information about heart on the following:
- Size of the chambers, volume and the thickness of the walls
- Pumping function, if it is normal or reduced to a mild/severe degree
- Valve function - structure, thickness and movement of heart’s valves
- Volume status as low blood pressure may occur as a result of poor heart function
- Pericardial effusion (fluid in the pericardium - the sac that surrounds the heart), congenital heart disease, blood clots or tumours, abnormal elevation of pressure within the lungs etc
How long does 2D Echocardiography take?
A brief exam in normal case may be done within 15-20 minutes. However, when there are heart problems, it may take much longer.
How safe is echocardiography?
It is absolutely safe. There are no known risks of the ultrasound in this type of testing.
To live healthy & happy, one must keep a check on the body’s functioning by going for regular health checkups. This helps in assessing risk factors and diagnosing diseases at an early stage, which will result in effective treatment and better management of the condition.