- 9975035364
- [email protected]
About Diabetes & its Treatment
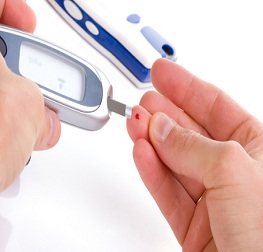
Diabetes is a chronic disease.
Chronic disease means a condition that is long term. A chronic disease can be stressful and may change the way a person lives and how they relate to others.
Most chronic conditions do not fix themselves and are generally not cured completely. Some can be immediately life-threatening, such as heart attack and stroke. Others linger over time and need regular management, such as diabetes. Most chronic illnesses stay throughout a person’s life, but are not always a cause of death, such as arthritis.
Diabetes is a condition where the amount of glucose in your blood is too high because the body cannot use it properly.
For our bodies to work properly we need to convert glucose (sugar) from food into energy in our muscles and organs, especially our brains!
Glucose is a sugar that comes from digesting foods which contain carbohydrate that is then absorbed into your blood. This is where the names ‘blood glucose’ or ‘blood sugar’ levels come from. Glucose is also stored and released in your body by the liver.
Blood glucose levels are normally controlled by a hormone called insulin which is made by the pancreas. Insulin acts as a key to unlock cells in the body to allow glucose to enter, where it (the glucose) can then be used as fuel for energy so we can work, play and generally live our lives.
Diabetes develops when glucose can’t enter the body’s cells to be used as fuel and builds up in the blood. This happen when either:
What are the Signs & Symptoms of Diabetes?